Achieving financial independence in your 30s is an ambitious yet increasingly attainable goal. In an era where traditional retirement ages are shifting and economic uncertainties abound, many young professionals are seeking ways to secure their financial future early. Financial independence means having sufficient personal wealth to live without obligatory work, granting freedom to pursue passions, hobbies, or entrepreneurial ventures without economic constraints.
In this article, we will explore actionable strategies backed by data, practical examples, and expert insights that illuminate how to establish financial independence in your 30s. Whether you’re climbing the corporate ladder, growing a business, or optimizing your spending, these steps can lead you toward a secure and autonomous financial life.
Understanding Financial Independence: Key Concepts and Mindset
Financial independence is more than just accumulating money—it involves conscious planning, discipline, and long-term vision. At its core, financial independence means your investments and assets generate enough income to cover all your living expenses indefinitely. This implies having a reliable cash flow from dividends, rental income, interest from savings, or profits from entrepreneurial pursuits.
Consider the popular rule known as the “4% rule,” which stems from the Trinity Study by financial experts. It suggests that if you withdraw 4% from your retirement portfolio annually, your funds can last for 30 years or more without depletion. For example, if your annual expenses are $40,000, you’d need $1 million invested to be considered financially independent. Understanding such metrics helps set clear targets.
Success stories abound, such as that of Pete Adeney (Mr. Money Mustache), who retired in his 30s after careful budgeting and aggressive saving. He emphasizes frugality combined with smart investing as the backbone of his early retirement. These examples demonstrate that with the right mindset and financial literacy, early independence is achievable.
Maximizing Income Streams: Diversify and Amplify Your Earnings
A fundamental pillar to reaching financial independence is increasing your income, not just relying on a salaried job. Many financially independent individuals in their 30s have multiple income streams, reducing vulnerability to market fluctuations or unemployment.

One practical approach is investing time and resources into side hustles or freelancing. According to a 2022 Gallup poll, about 45% of U.S. workers engage in part-time or freelance work, elevating their earning power. For instance, a software engineer might code apps in their spare time or conduct online classes, effectively doubling income streams.
Another example is real estate investing. Building rental property portfolios can create passive cash flow that accumulates wealth over time. Take the case of Sarah and Michael, who bought their first rental in their late 20s. By the time they reached 35, they owned five units that covered their mortgage and provided a net positive income. Real estate, when leveraged responsibly, can serve as both an appreciating asset and a consistent income generator.
High-income professions naturally make financial independence easier to achieve, but even moderate incomes can reach similar goals through diversification. Table 1 illustrates the potential impact of adding side income on overall wealth accumulation.
| Income Category | Primary Income (Annual) | Side Income (Annual) | Combined Annual Income | Potential Savings Rate (%) | Approximate Portfolio Growth (5 years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate ($50,000) | $50,000 | $10,000 | $60,000 | 30% | $90,000 |
| High ($100,000) | $100,000 | $20,000 | $120,000 | 40% | $240,000 |
| Entrepreneurial ($150,000) | $150,000 | $50,000 | $200,000 | 50% | $500,000 |
*Table 1: Comparative Impact of Side Income on Savings and Wealth Accumulation*
Increasing income efficiently also means upskilling or switching careers to high-demand fields. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (2023) reports that median wages in technology, healthcare, and financial services exceed $80,000, offering higher savings potential.
Smart Budgeting and Expense Management
While boosting income is critical, controlling and optimizing expenses ultimately determines how much you can save and invest. This does not imply living a restrictive life but rather cultivating financial awareness and making intentional choices.
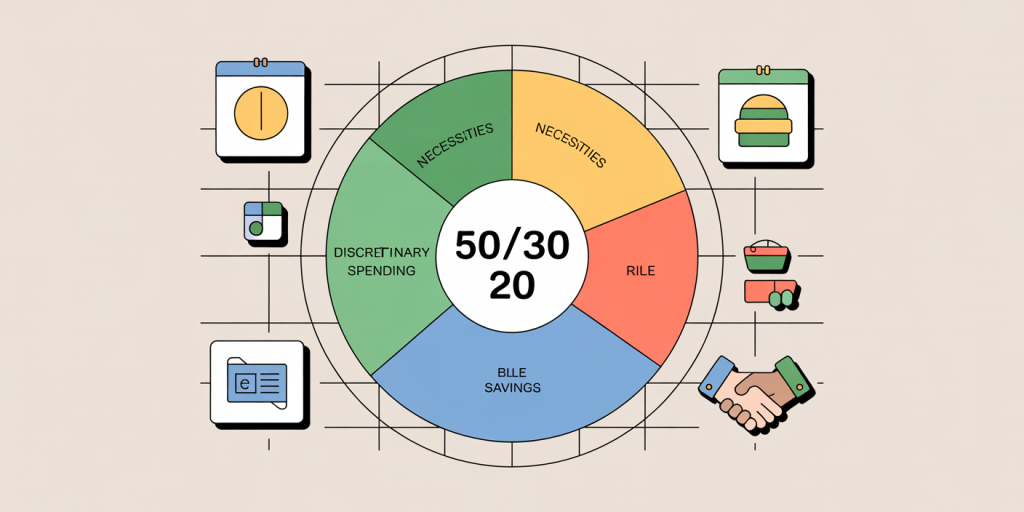
Creating a detailed budget — tracking fixed costs (rent, loan payments) and variable costs (food, entertainment) — is step one. Many financially independent individuals follow a 50/30/20 rule: 50% for necessities, 30% for discretionary spending, and 20% for savings and investments. This model provides balance and sustainability.

Look at Mark, a 33-year-old teacher who managed to cut unnecessary subscriptions and cook meals at home, trimming monthly expenses by 25%. He redirected this saved money into tax-advantaged retirement accounts such as 401(k) and IRAs. His disciplined spending combined with employer matching significantly boosted his savings rate.
Expense optimization requires examining recurring costs and lifestyle inflation. Data from the U.S. Federal Reserve suggests that millennials spend about 15% more annually on lifestyle upgrades than previous generations, which can slow wealth accumulation. Delaying luxury purchases (like new cars or expensive vacations) until your portfolio is more robust can accelerate independence.
Additionally, consider negotiating bills such as insurance premiums, utilities, or phone plans. Small monthly reductions compound into thousands of dollars saved over years. Apps like Truebill or Trim can help identify unnecessary expenses automatically.
Investing Wisely: Building a Robust Portfolio Early
Investing is the cornerstone of wealth growth that can outpace inflation and generate passive income. Starting early leverages the power of compound interest, famously described by Albert Einstein as the “eighth wonder of the world.”
You don’t need to be an expert to begin. Index investing through funds like the S&P 500 has historically offered average annual returns of 10%. According to Vanguard and Fidelity data, individuals who consistently invested 15% of their income in diversified portfolios early on had significantly higher net worths by age 35 compared to peers who started later.
Consider Emily, who began putting $500 monthly into a low-cost index fund at age 25. By 35, her portfolio grew to over $90,000 without additional lump sums. Contrast this with James, who saved the same amount each month but only started investing at 30; by 35, James had roughly half the portfolio size.
Beyond stocks, incorporate bonds for stability and real estate for diversification. Roth IRAs and employer-sponsored plans often offer tax advantages, accelerating net returns. Financial advisors suggest a diversified portfolio split roughly into 80% stocks and 20% bonds for people in their 30s, gradually shifting toward bonds with age to reduce risk.
| Investment Vehicle | Average Annual Return | Risk Level | Liquidity | Tax Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S&P 500 Index Funds | ~10% | Moderate to High | High | Tax-deferred in retirement accounts |
| Bonds (Treasuries) | ~3-5% | Low | Moderate | Tax advantages in some cases |
| Real Estate | ~8-12% (incl. rental income) | Moderate | Low | Depreciation and tax deductions |
| Cryptocurrency | Highly Volatile | Very High | High | Limited current tax clarity |
*Table 2: Comparative Overview of Common Investment Vehicles*
Managing Debt and Using Leverage Strategically
Debt is a double-edged sword; it can either derail financial independence or accelerate asset acquisition if used intelligently. Young adults frequently carry student loans, credit card debt, or mortgages, which need effective management.
High-interest debts such as credit cards should be paid off immediately to prevent interest compounding against your savings. For example, an 18% APR on a $10,000 credit card balance can add $1,800 in interest annually, severely impacting available capital for investing.
Conversely, mortgages and business loans, if approached prudently, can be tools for wealth building. Take the example of Robert, who bought a fixer-upper property with a 30-year mortgage at 3.5% interest. After renovations, the property’s value rose 20%, and rental income surpassed mortgage payments, building equity while generating positive cash flow.
Managing debt also involves refinancing options in low-interest environments and consolidating debts to improve cash flow. According to Experian’s 2023 report, individuals who refinance personal loans and mortgages at lower rates save thousands over the term of the loan.
Future Perspectives: Sustaining and Growing Wealth Beyond Your 30s
Once financial independence is attained in your 30s, the focus shifts toward sustaining and growing your wealth in alignment with evolving personal and economic contexts. Inflation, changing tax laws, and financial goals require continuous education and portfolio adjustments.
Emerging trends like ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing and the rise of digital assets offer new avenues but also bring novel risks. Diversification remains key; consider expanding into international markets and alternative investments with professional guidance.
Moreover, building wealth is also about legacy planning—estate planning, trusts, and insurance help protect your assets and provide for dependents. The younger you start, the more benign tax repercussions can be through gifting strategies and early retirement account contributions.
Ultimately, mindset and flexibility form the backbone of long-term success. Regularly reviewing finances, adapting strategies, and embracing lifelong learning help ensure your financial independence is not just a temporary milestone but a sustainable way of life.
Achieving financial independence in your 30s is a multi-faceted journey involving increased income, strategic budgeting, disciplined investing, and smart debt management. By adopting the habits and tactics outlined here, you set a foundation to live life on your terms — financially secure, free, and fulfilled.

Deixe um comentário