Choosing the right auto insurance policy is crucial for protecting your vehicle, finances, and personal liability. With countless providers and policy options available, understanding how to effectively compare auto insurance policies can save you money and ensure you receive adequate coverage. This article outlines the essential factors to consider when analyzing and comparing auto insurance policies, supplemented by real-life examples, data-driven insights, and practical tools like comparative tables.
Understanding the Basics of Auto Insurance
Auto insurance covers various risks associated with operating a vehicle, including accidents, theft, and liability for injuries or damages caused to others. Policies typically feature different coverage types such as liability, collision, comprehensive, personal injury protection (PIP), and uninsured motorist coverage. Each of these components serves a unique purpose, and the balance between them impacts both protection and cost.
For example, liability coverage is mandatory in almost all states, protecting the insured against claims for bodily injury or property damage to others. In contrast, collision insurance covers damages to your vehicle after a crash, regardless of fault. Comprehensive insurance encompasses coverage for non-collision incidents like theft, fire, or natural disasters. Understanding these differentiations allows consumers to tailor policies according to needs, driving habits, and vehicle value.
According to the Insurance Information Institute, the average annual auto insurance premium in the United States was approximately $1,674 in 2023, but prices can range significantly based on location, driving record, and coverage selections. This variance underlines the importance of comparison shopping to find the best value.
Key Factors to Compare in Auto Insurance Policies
When comparing policies, focusing on certain critical elements ensures that you consider both price and protection quality. These key factors include coverage limits, deductibles, premium costs, exclusions, and customer service reputation.
Coverage Limits and Types Coverage limits indicate the maximum amount an insurer will pay under a policy. For liability, minimum state requirements often apply, but purchasing higher limits can provide better financial protection. For example, New York requires minimum liability coverage of $25,000 per person and $50,000 per accident; however, a policy with $100,000/$300,000 limits offers considerably more security. Moreover, examine whether policies offer optional add-ons such as roadside assistance or rental car reimbursement, which can enhance convenience after incidents.
Deductibles The deductible is the amount the insured must pay out-of-pocket before the insurer covers damages. Policies with higher deductibles generally feature lower premiums but require more upfront costs during claims. A practical example is a driver with a $500 deductible paying a monthly premium of $120 versus a $1,000 deductible policy costing $90 per month. The decision depends on the consumer’s comfort with potential out-of-pocket expenses.
Premium Costs The premium is the recurring payment to maintain the policy. Comparing premiums involves more than just the sticker price; it’s vital to evaluate the relationship between premium size, deductibles, and coverage comprehensiveness. Using online tools and calculators, consumers can obtain personalized quotes reflecting driving history and vehicle details.
Exclusions and Limitations Insurance policies often contain exclusions—situations or damages not covered. For instance, some policies exclude coverage for customized parts or future rental car fees above a specified daily limit. Reviewing these exclusions can prevent unwelcome surprises after a claim.
Reputation and Customer Support Beyond contract details, insurer reputation for claim handling, customer service responsiveness, and financial stability matters. According to J.D. Power’s 2023 U.S. Auto Insurance Study, companies like Amica Mutual and State Farm score highly for customer satisfaction, while lesser-known providers may offer competitive rates but with inconsistent service quality.
Comparing Policy Features with Real Examples
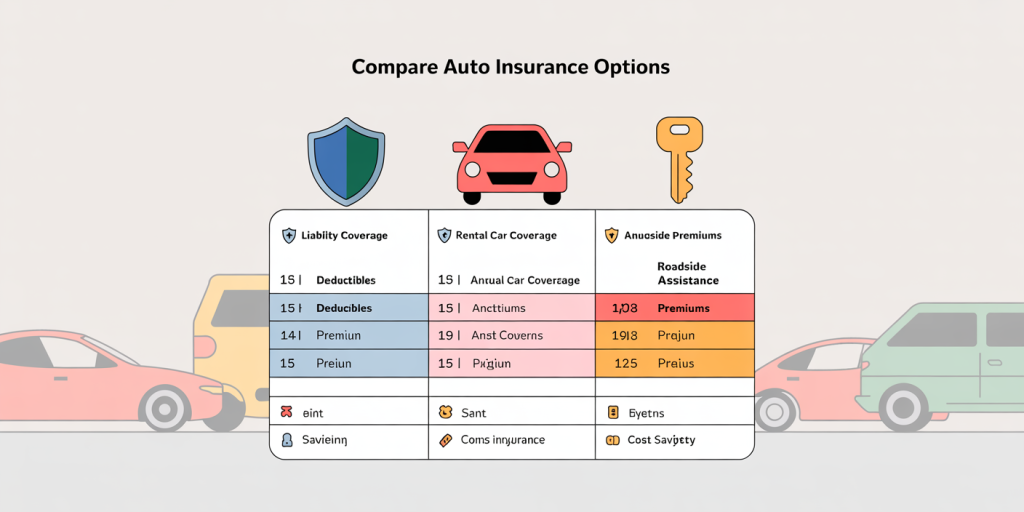
Consider three hypothetical policies—Policy A, Policy B, and Policy C—from different insurers for a 30-year-old driver in California with a clean record. The table below summarizes their key features:
| Feature | Policy A | Policy B | Policy C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liability Coverage | $50,000/$100,000 | $100,000/$300,000 | $25,000/$50,000 |
| Collision Deductible | $500 | $1,000 | $250 |
| Comprehensive Deductible | $500 | $1,000 | $250 |
| Rental Car Coverage | Up to 30 days | No | Up to 15 days |
| Annual Premium | $1,100 | $1,350 | $950 |
| Roadside Assistance | Included | Not included | Included |
Policy A offers balanced coverage with moderate deductibles and rental car inclusion at a reasonable premium. Policy B emphasizes higher liability limits but charges a higher premium with no rental car option. Policy C is the cheapest but has the lowest liability and highest risk exposure.
Practical example: A driver choosing Policy C might face greater financial risk in a severe accident, despite saving $150 annually compared to Policy A. If the driver anticipates occasional long-distance travel requiring rental vehicles, Policy A’s inclusion might be more valuable.
Utilizing Online Tools and Aggregators
In the digital age, consumers have access to numerous online resources to aid in policy comparison. Insurance aggregators like The Zebra, Compare.com, and NerdWallet let users input personal and vehicle information and receive multiple quotes quickly.
Using these tools streamlines the comparison process but requires discernment. Some aggregators display sponsored policies preferentially, so cross-checking quotes directly through insurer websites is recommended. Additionally, user reviews and ratings available on platforms like Trustpilot offer insights into insurer reliability.
Consider the real case of Sarah, who compared car insurance for her 2019 Honda Civic using three aggregators and found a $200 difference in annual premium quotes for similar coverages. She later called insurers directly and negotiated a further $150 discount by bundling with renters insurance.
Analyzing Discounts and Special Offers
Most insurers provide various discounts to lower premiums. These may include safe driver discounts, multi-policy bundling, good student discounts, low mileage discounts, and more. Understanding and leveraging these discounts can substantially reduce premiums without sacrificing coverage quality.
Data from the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) reveals that bundling auto and home insurance can reduce individual premiums by up to 15%. Furthermore, completion of defensive driving courses often qualifies drivers for 10% to 20% discounts in many states.
An example is John, a 45-year-old professional with clean driving history who realized a total savings of $300 annually by switching to an insurer offering both auto and home coverage plus a safe driver discount, compared to his previous policy.
Evaluating Claim Processes and Financial Strength
A crucial aspect often overlooked in policy comparison is the insurer’s claim process efficiency and financial robustness. Prompt, fair claim settlements protect policyholders from prolonged disruptions and financial loss.
The National Association of Insurance Commissioners reports that the average auto insurance claim settlement time is about 30 days, but some companies resolve claims in as little as 10 days. Additionally, insurers rated “A” or higher by A.M. Best have proven ability to meet financial obligations, which is essential in catastrophic events.
For example, during Hurricane Harvey in 2017, insurers with high financial strength ratings absorbed massive claims with minimal delays. Customers of weaker-rated companies experienced longer wait times and claim denials due to insolvency concerns.
Future Perspectives in Auto Insurance Policy Comparison
The auto insurance market is rapidly evolving due to technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting consumer preferences. Usage-based insurance (UBI), powered by telematics devices or smartphone apps, allows premiums to be determined by actual driving behavior, such as miles driven, speed, and braking patterns. This innovation offers personalized pricing and greater transparency.

Moreover, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly applied to claims processing, fraud detection, and risk assessment, improving efficiency and cost savings that may trickle down to consumers.
For consumers, future comparison methods may become more integrated and dynamic. Real-time data could enable instant policy adjustments, while blockchain technology might enhance transparency in contract terms and claims history.
States are also revising minimum coverage requirements reflecting increasing repair costs and evolving vehicle technologies such as electric and autonomous cars. This trend will push insurers to offer more tailored, inclusive policies with better digital tools for comparison.
The rise of environmental concerns is prompting insurers to develop green car discounts or policies incentivizing the use of electric vehicles. Over the next decade, these factors are expected to reshape the auto insurance landscape, making consumer education and comparison even more vital.
Choosing the right auto insurance policy requires a comprehensive approach balancing coverage needs, cost, insurer reliability, and future adaptability. By understanding policy components, comparing key features, leveraging discounts, and considering the insurer’s claim process and financial health, consumers can make informed decisions. Staying informed about emerging trends and technologies will further empower drivers to secure optimal protection in a rapidly changing auto insurance environment.

Deixe um comentário